To consider an application for financing, fill out the form and send it to us by e-mail along with the project brief, or contact our experts
Project finance lending plays a critical role in the development of such projects, being the main way to provide funds for the construction, expansion and modernization of factories, power plants, seaports, roads and pipelines.
Skywalk Investment Group, a company with international experience, specializes in lending and project finance services for large businesses.
We are ready to offer clients with loans from 50 million euros with a maturity of up to 20 years on the most attractive terms in your sector.
The list of our offerings also includes financial modeling services, bank guarantees, project management, investment engineering, industrial engineering, consulting and much more.
Thanks to broad competencies, international business contacts and rich practical experience, our financial team successfully implements projects in most countries of the world. Share your investment plans and learn more about our advantages.
The essence of project finance lending
PF is the most difficult method of financing in terms of organization and planning.This method is applicable to projects whose value significantly exceeds the current assets of the initiators. The reason is that it is extremely difficult for project sponsors to convince a financial institution to borrow more than the value of their entire business.
Loan terms in project finance are set according to the expected cash flow, so the maturity, interest and fees associated with the repayment of loans are adjusted individually depending on the specific project and its market.
At present, the capitalization of the banking system of the USA, Great Britain, as well as Spain and other developed European countries makes it possible to issue loans for capital-intensive projects.
However, in the case of loans exceeding several hundred million euros, syndicated loans are often used, including those issued by international consortiums.
Banks and large banking consortiums are the main lenders that provide debt financing for large projects in the form of a principal loan or a subordinated loan.
Project finance (PF) uses a wide range of alternative and complementary financing schemes that share common features.
The concept of project finance for large business projects does not depend on the creditworthiness of shareholders (sponsors) and the value of assets involved in a particular project. This tool allows businesses to finance bold ideas based on forecasting financial flows and profitability. In other words, the decisive factors in project finance lending are the forecasting of the effectiveness of a particular project and the assessment of its risks, but not the financial health of its sponsors.
In a sense, this is a violation of the fundamental principle of corporate finance, according to which the key requirement for lending is the reliability (creditworthiness) of the borrower.
The distinctive feature of project financing is the possibility of issuing a loan for large projects without regard to the positive financial history of the borrower.
Debt incurred on a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) created by sponsors for a specific project is not reflected in their balance sheet. For sponsors, this means the off-balance sheet nature of the debt, which is consistent with the principle of limited liability of shareholders and is associated with increased creditworthiness.
SPV debt does not burden the financial statements of member companies, or shareholders.
On the other hand, the existing financial obligations of the shareholders do not have a direct impact on the debt of the Special Purpose Vehicle and its current operations.
An indirect connection between the reputation of the participants and the financing of the project still exists. Although project finance is based on lending to companies without a long credit history, the creditworthiness of the company's shareholders is taken into account by the potential lender and reflected in the terms of the loan agreement.
The ability of the new entity to incur debt may be higher in the case of project finance, as the high proportion of debt in the project's capital structure allows participants to use high financial leverage.
This imposes certain requirements on the professional management of the project and creates the prerequisites for more active participation of the lender at all stages of the project life cycle. The intervention of the lender covers all stages of the project, up to the repayment of the loan with the corresponding interest. Strict control over investments requires the establishment of an independent company that "isolates" this project from other activities.
The risks, profits and responsibilities of each of the participants in project finance schemes must be legally and economically separated in order to ensure effective project management at all stages.
Differences between PF and corporate lending
Project finance lending is based on specific methods of risk analysis and protection of participants' interests.Unlike traditional methods of corporate lending, it is initially impossible to adequately assess the future financial results and assets of a company created to implement a specific project.
In corporate lending, the bank pays attention to the following:
• The financial health of the borrower, assets and creditworthiness, which means the ability to repay the principal and interest under the loan agreement within the specified time frame.
• Key financial parameters of the investment project, its advantages and risks for the borrower in the context of their impact on creditworthiness.
In project finance lending, the bank evaluates the following aspects:
• An investment project in terms of efficiency, profitability and benefits for its participants.
• The reputation of the project participants in terms of their creditworthiness and professional competencies, their ability to obtain the predicted benefits from the project.

In the case of corporate lending, we deal mainly with the assessment of the borrowing company, but in the second case (PF), the investment project assessment comes first.
The order, content and volume of the analyzed questions are radically changing.
The corporate finance model for large projects is based on separating bank risk from project risk. Credit risk is identified with the solvency of the borrower and the value of the collateral offered, regardless of the success or failure of the financed investment project.
The PF usually does not include borrower checks or only minimally includes them. In this case, the borrower arranges the financing scheme in such a way as to meet the strict requirements of all the parties involved in the project, primarily banks.
The reliability of sponsors, contractors and other business partners associated with investments is carefully evaluated. In both cases of corporate and PF lending, the risk and possible causes of its occurrence are carefully studied, and measures to minimize it are developed.
In project finance, the risk of a bank is in practice equal to the risk of a given investment project.
The analysis of credit risk is carried out in terms of the total return and debt servicing capacity of the SPV on a current basis. This analysis is based on capital structure and debt coverage ratios.
In addition to the difference in the order and volume of analyzes and studies carried out in corporate lending and PF, experts point out another difference in the procedure for obtaining a large loan.
The traditional framework procedure is as follows: the borrower learns the terms of the loan, applies for the loan, and accepts the bank's decision. Since in the case of PF there is no borrower at the very beginning of the project organization process, the approach to obtaining a loan is changing.
The terms of the loan affect the profitability of the investment, so the sponsors expect the bank to initially evaluate the project in terms of the correctness of its assumptions. In PF models, lenders can assess the investment risk of a project before the SPV is established, and sponsors will take the necessary steps to adjust the investment vehicle when they hear the lender's opinion.
The above considerations show that, compared to traditional financing methods, project finance can be a more expensive solution. These will be higher interest rates and higher fees as the terms of the loan are overly flexible and the risk is much higher.
Planning and organizing lending in project finance
The main stages of deal preparation and project evaluation are presented below:1. Analysis of the project, including the identification of potential risks, their assessment and the development of practical measures to minimize and control them.
2. Optimization of the project financing structure, including the share of sources of debt financing, the size and form of the authorized capital of the SPV.
When evaluating an investment project by a bank, four types of analyzes can be distinguished, covering various areas.
These are technical analysis, financial analysis, reliability analysis of project participants, identification and distribution of risks.
The technical analysis evaluates the technological feasibility and operational efficiency of the project. Among other things, the expected costs, the investment period, the technical parameters of the facility, the expected operating costs, and the compliance of the planned facility with environmental protection standards are checked.
Economic and financial analysis is used to objectively assess the sufficiency of the projected financial flow generated by the project to service the debt.
This analysis provides an answer to the question of whether the remaining funds will be a satisfactory reward for investors.
The main risk assessment tools are financial analysis based on cash flow forecasting, as well as debt service ratio calculation and sensitivity analysis. To evaluate the project, lenders use such financial indicators as the rate of return and cost of capital, payback period, NPV, IRR and others. In these studies, discounted cash flow methods, sensitivity analysis, scenario and simulation modeling play an important role.
When accepting increased project risk, the lender applies more sophisticated procedures to evaluate the effectiveness and risk of investments.
Identifying potential threats is critical as any unidentified risk remains uncovered and exposes the bank to excessive risk.
The high profitability of the project, taking into account the risk, is a necessary but not sufficient condition for lending. The bank should conduct a credit risk analysis based on the assumption that the main threat is a decline in the borrower's ability to service credit. This analysis is based on debt structure and debt coverage.
The Risk Identification and Allocation Analysis includes elements of all analyzes and summarizes them. Among other things, financial experts identify and evaluate individual types of risk, after which a risk distribution diagram is developed. Individual project finance participants are assigned risks that they can most effectively take on (for example, an engineering company can most effectively control construction risks).
The reliability analysis of project participants covers their goals, responsibilities and experience.
The idea of increasing security in project finance lending is based on a professionally developed system of responsibilities for each of the participants, so a competent contractual structure is the basis for the success of the project.
Development of a loan agreement
Large loans in project finance mean high risk for capital providers.Of course, the decision to issue such loans will be based on a number of analyzes and examinations, and is usually associated with tightening the terms of the loan (terms, debt repayment procedure, interest).
Figure: Stages of developing a loan agreement in project finance.
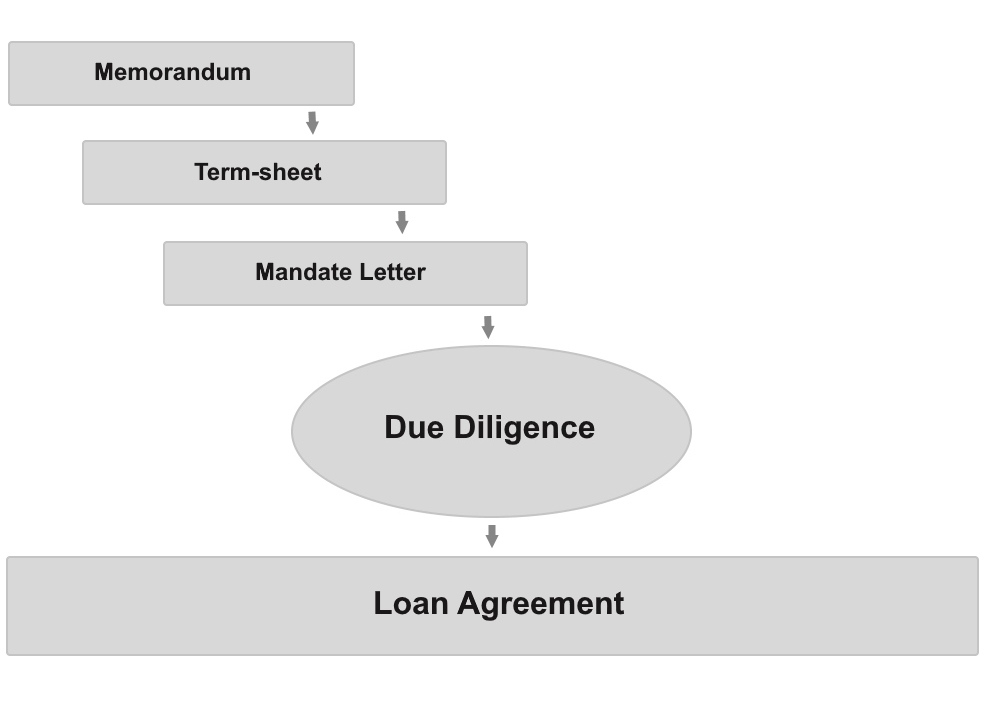
The bank's conclusion on the possibility of providing credit funds can be made after a preliminary review of the project documentation.
The consent of creditors is expressed in the form of an official document that defines the main terms of the loan (Head of Terms), which contains the following:
• Loan amount.
• Loan maturity.
• Loan interest and bank charges.
• The procedure for transferring funds.
• Debt repayment procedure.
• Loan security (if applicable).
Head of Terms in the preparatory period helps to verify the assumptions of the feasibility study and the correct definition of the capital structure of the special project company.
Since the issuance of this document, the chances for the implementation of the project will increase many times over, and in the future this financial document becomes the basis for the development of a loan agreement.
From the sponsors' point of view, preparation for financing a capital-intensive project begins with the hiring of a professional consultant who prepares a memorandum and a list of entities that can be invited to tender. The investment memorandum contains a detailed description of the company and its environment, a detailed financial model of the enterprise.
The so-called Term-sheet lays the foundation for future negotiations with creditors.
Loan agreements in project finance are very extensive and vary widely from bank to bank.
Therefore, the more accurate the request, the greater the influence of the company on the future loan agreement.
If the loan agreement will be based on international law, it is advisable to hire consultants who specialize in the law of the host country and at the same time have a local office. In the case of capital-intensive projects, when choosing banks for a financial consortium, it is worth choosing a bank that is well acquainted with local legal realities.
The second element in preparing for a project finance loan is the Mandate Letter.
This document includes, among other things, the following elements:
• Terms of the loan agreement specified in the Term-sheet.
• Mode of fulfillment of contractual obligations by the parties (best effort or underwritten).
• Duration of the agreement: the longer it is, the higher the chance of avoiding a situation in which the bank can initiate changes in terms.
• Exceptional clauses: for example, the so-called Market Adverse Change Clause allows the bank to withdraw from the contract in the event of a sudden change of market conditions, which is a highly unfavorable clause for project sponsors.
In the next step, the SPV signs a contract with a law firm.
The latter acts on behalf of the bank and carries out due diligence of the project (these services are paid for by the bank). Next, the company and its consultants, representatives of the bank and their lawyers enter into negotiations. The decisive moment is the signing of the loan agreement, which establishes the obligations of the participants until the project is finished and the loan is repaid.
A loan agreement in project finance typically includes the following:
• Conditions for granting financing.
• Rules for repayment of the main part of the loan and interest payments.
• Financial conditions that the borrowing company undertakes to comply with.
• The method and frequency of the borrower's reporting to the bank.
• Conditions that allow the bank to terminate agreements and demand immediate repayment of the loan or seizure of assets that were provided as collateral.
• Certificates, acts and statements that ensure the fulfillment of the contract.
An important part of the lending procedure is the development of loan security conditions.
In the case of project finance, securing a loan with SPV shares makes it possible to sell assets as soon as possible in the event of the borrower's insolvency (project failure).
Project finance lending is a fairly flexible and efficient tool that ensures the effective implementation of expensive and risky projects based on future financial flows. This mechanism is quite developed, provided with a solid regulatory framework and is widely used in various industries around the world.
In project finance, we are dealing with a high flexibility of conditions, where the basis for minimizing risks is the cash flow (income) received from investments.
However, the lender does not completely abandon the traditional methods of securing a loan, such as bank guarantees and collateral.
Adequate cash flow and collateral allow banks to take on project risk.
If you are interested in long-term lending and project financing in the fields of energy, heavy industry, infrastructure, real estate, mining or processing of minerals, please contact the SWIG team.
We provide a full range of project finance services, including the establishment and management of SPV, financial modeling, project management, and a range of engineering and consulting services for large businesses.