To consider an application for financing, fill out the form and send it to us by e-mail along with the project brief, or contact our experts
The choice of a particular method largely depends on the financial health of the borrower, goals and scale of lending.
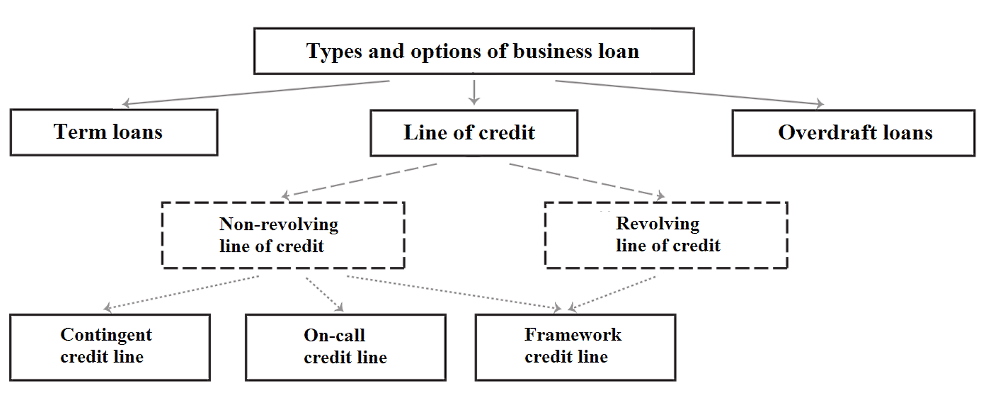
In banking practice, the most common methods of lending to business are the line of credit (LOC), overdraft and term loan (for example, investment loan), as shown below.
Each of these approaches differs in its specific features that are suitable for a particular area of the company.
Also, the choice of lending options depends on the nature of the financed project.
One-time term loan is a traditional way of business lending, which is characterized by a simple procedure for providing funds, clarity and consistency in the organization of the lending process.
This type of loan is used in cases where the company needs additional resources at once, ie the client receives the full amount at once as specified in the loan agreement.
The line of credit differs from the classic loan in that the disbursement of credit funds is in certain parts (tranches) within the established limit, as the borrower needs financial resources. This implies a longer and closer cooperation between the borrower and the bank, constant monitoring and analysis of financial needs.
An overdraft loan is used to eliminate payment gaps that arise in economic activity, ie it can be used only for a short period of time.
Line of credit (LOC)
A line of credit is a financial resource provided by a bank in tranches, usually on a targeted basis to meet current needs within a set limit over a period of time specified in the loan agreement.The term of the credit line agreement is determined based on the specific objectives, but, as a rule, this period usually varies from 1 to 3 years.
The interest rate for the use of a credit line is set by agreement of the parties, but may not be lower than the base rate. The cost of using credit resources, in addition to interest on the loan, may include a bank fee. Processing of documents is carried out once when concluding an agreement on opening a loan account. In the future, the borrower only uses the loan within the credit limit for the purposes specified in the agreement, without additional processing of documents for the loan.
The credit limit may be revised by agreement of the parties both at the request of the bank (for example, in case of deterioration of the borrower's financial health, reduction in the cost of collateral) and at the request of the borrower (for example, in increasing production and turnover).
In case of deterioration of the financial balance of the borrower, the bank has the right to stop the next tranche for a certain period, or stop cooperation altogether and demand early repayment of previously obtained funds, which must be stipulated in the loan agreement.
The credit line can be issued in the following cases:
• Permanent and predictable nature of business activities.
• Convenient opportunity for quick receipt of small tranches for long periods of time.
• Saving time by drawing up one agreement instead of drawing up several documents.
The method of calculating the credit limit is determined by banks, but the main criteria include the parameters of the turnover of the borrower's assets, the presence of seasonal factors of production, the level of working capital and more.
An example of calculating the credit limit for an industrial enterprise is given below:
CL = (In + UP + FP + Res + SG) – (Pa + Eq)
CL – credit limit,In – inventories,
UP – unfinished production,
FP – finished products,
Res – receivables,
SG – shipped goods,
Pa – payables,
Eq – equity.
This loan instrument allows the client to use more funds than available on the current account.
Repayment of loans under this program occurs automatically with any receipt of funds on the current account. First of all, interest is repaid, and the remaining amount is used to repay the principal debt. This makes the credit line a very convenient financial mechanism for numerous companies engaged in active production and investment activities.
The advantages of the loan under the concept of the credit line is that the borrower is given the opportunity within the established limit to use borrowed funds at the time of need.
This, in turn, significantly reduces the cost of servicing the loan.
Revolving and non-revolving credit line
A credit line for a business can be revolving or non-revolving.Non-revolving credit line means that the loan amount is transferred to the company's current account in certain tranches.
The amounts and dates of specific tranches are specified in the loan agreement or determined in real time on the basis of the borrower's applications. After the transfer of the entire amount, the limit is closed and the borrower can not use it a second time.
The pros and cons of a non-revolving credit line are listed below:
|
Pros
|
Cons
|
| Interest is charged only on used tranches, ie interest is not charged on the balance limit, which the borrower did not use. | In case of difficulties with repayment of the previous tranche, the bank may reduce or close the credit limit until its full use. |
| The cash disbursement fee is usually charged separately for each tranche, eliminating the need to pay a large sum at once. | Banks may impose an additional fee on unused credit line limit. |
| Early repayment charge is usually absent. | Repayment schedules are set for each tranche separately, the annuity schedule is often absent. |
Revolving credit line is a lending scheme that allows the borrower to receive funds periodically within a pre-set limit as needed during the term of the credit line, repaying all or part of the amount.
As the credit line is used, the borrower's debt decreases, and the credit limit is restored. In this case, the borrower has the opportunity to obtain the next part of the loan.
A credit line with an issuance limit assumes that the borrower can receive credit only a certain number of times. The total amount of all tranches may not exceed the established credit limit.
A credit line with an issuance limit is used for the following purposes:
• Purchase of assets to expand production (including equipment, transport, buildings).
• Purchase of materials, goods and services, wages, replenishment of working capital.
A credit line with a debt limit means that the borrower can re-use the loan after the debt is repaid, with only the amount of the debt being limited and no limit on the issuance of funds.
The sooner the borrower repays the money, the sooner he will get a new loan. A credit line with a debt limit is appropriate if the company periodically needs short-term borrowing.
Framework (target) credit line means that the bank is ready to quickly enter into credit agreements or open credit lines in a predetermined amount and on previously established terms. Such a credit line is typically used by businesses to pay for deliveries under contracts that run over a period of time, as well as to finance the costs associated with implementing targeted commercial programs.
The pros and cons of a framework credit line are shown below.
|
Pros
|
Cons
|
| It is not necessary to agree on the allocation of funds each time, and the borrower determines the loan within the limit set by the agreement. | The bank may levy a fine or charge a penalty for unused funds up to the credit limit |
| The borrower uses as many credit resources as he needs, which reduces the cost of debt service. | |
| Debt repayment is carried out automatically upon receipt of funds on the current account of the borrower company. |

Overdraft
Another interesting loan instrument for current business activities is overdraft lending.Overdraft means a short-term loan within the limit set by the bank, which allows the company to cover transactions in amounts exceeding the current account balance.
An overdraft loan can be issued for a decade, a month or a year, depending on the needs of the borrower and the type of overdraft. Movable and immovable property of the borrower, bank guarantees, financial guarantee of third parties may act as collateral for the overdraft. An overdraft can also be provided without any collateral (so-called blank overdraft).
Overdraft is not targeted financing, ie the borrower determines the distribution and purpose of the use of borrowed funds.
The advantage of overdraft for banks is the ability to demand repayment of the loan at any time. On the other hand, the client receives low interest rates, the ability to freely use borrowed funds, as well as preferences for regular customers in the form of lower interest rates or higher credit limits.
The overdraft limit is the maximum allowable amount of actual debt at any given time. Each bank can use its own method of calculation, and the limit set by the bank depends more on the financial health of the borrower and his credit rating.
Types of overdraft and options for calculating the limit are given in the table below.
|
Types of overdraft
|
General description
|
Formula
|
| Standard overdraft | The loan is provided to the client within the established limit for the execution of his payment orders and payment of costs associated with their execution, despite the lack of funds in the account | L = T / 2 |
| Overdraft in advance | The loan is provided to a client who meets the requirements of the bank, in order to attract (return) it for settlement and cash service | L = Tm / 3 |
| Overdraft for payment | The loan is provided to customers who meet the requirements of the bank and at least 75% of turnover is collected revenue (including deposited in the current account). | L = I / 1.5 |
| Technical overdraft | The loan is provided to the client without taking into account his financial health, for payments made to the borrower's account (sale / purchase of currency on the stock exchange, before the return of a term deposit or other guaranteed receipts on the client's account). After receiving funds on the client's account, the technical overdraft is closed. | L = 0.95 x S |
L – estimated overdraft limit,
T – the minimum monthly credit turnover on the client's current account,
Tm – the minimum monthly credit turnover minus future debt repayment,
I – the minimum monthly amount of the client's cash receipts,
S – guaranteed receipts to the client's account within the next 3 days.
The terms of using the overdraft depend on the bank's credit policy.
One of the options is that interest for using the overdraft is accrued once a month on the actual debt and for the actual term of the loan (fact / 365 days) and must be paid in the month in which they are accrued. Interest is repaid daily automatically from the current account, which operates in overdraft mode.
The bank charges a penalty and increased interest for late repayment of the loan on the overdraft.
An overdraft is essentially similar to a standard loan, but it has a number of advantages.